一、核心概念:
电动执行器: 提供旋转或直线运动的动力源。
二级传动涡轮箱: 指包含两级蜗轮蜗杆减速机构的齿轮箱。
蜗轮蜗杆传动: 利用蜗杆(类似螺杆)驱动蜗轮(类似斜齿轮)实现大减速比和运动方向改变(通常90度)。
二级传动: 意味着有两套这样的蜗轮蜗杆副串联工作,以实现更大的总减速比。

二、核心计算公式


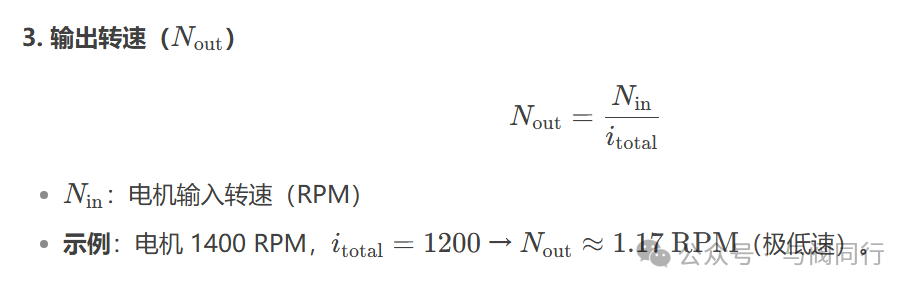

三、二级传动损耗比详解
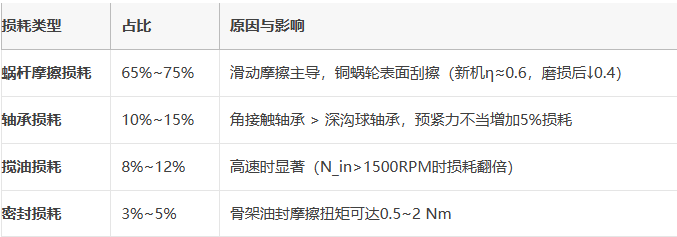
总效率η_total = η1×η2×η轴承×η密封
新机效率:0.45~0.55(精密研磨蜗杆+锡青铜蜗轮)
老化后效率:↓0.25~0.35(运行3年后,润滑劣化+齿面磨损)
警告:计算扭矩必须按 η_total=0.3~0.4 选型,否则可能带不动负载!
四.选型注意事项(避坑指南)
(1)
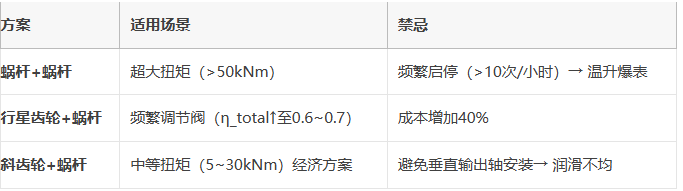
(2)材料与工艺要求
蜗杆:20CrMnTi渗碳淬火(硬度HRC58-62),表面粗糙度Ra≤0.8μm
蜗轮:ZCuSn10P1离心铸造,禁止用铸铝替代!
润滑脂:聚脲基合成脂(适用温度-30~180℃),填充量≤箱体容积50%(过多加剧搅油)
(3)热管理措施
箱体表面积:按Q_loss = (1-η_total) × P_in计算发热量
强制散热要求:
P_in > 15kW \quad \Rightarrow \quad \text{加散热鳍片} \\
P_in > 30kW \quad \Rightarrow \quad \text{强制风冷(风扇功率≥5%P_in)}
(4)自锁可靠性验证
自锁条件:蜗杆导程角γ < arctan(μ) (μ≈0.05~0.12)
测试要求:在1.5倍T_required下保压10分钟,位移≤0.5°
四、成本优化策略
(1)替代方案对比
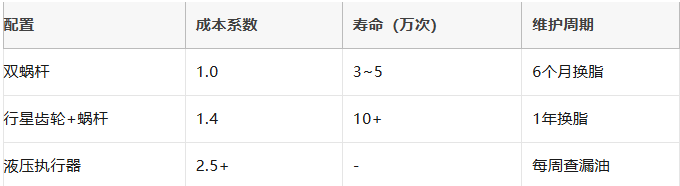
(2)降本技巧
非关键阀:用 斜齿轮+单蜗杆(η_total≈0.5,成本↓30%)
中轻载阀:输出级改用尼龙蜗轮(承载↓40%,但成本↓50%)
五、故障预警指标
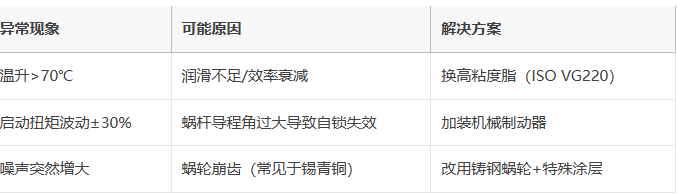
六.工程应用中的计算示例



